
Membrane Distillation
What’s Membrane Distillation?
Membrane Distillation (MD) is considered as one of major emerging techniques for sepration of ono-volatile solutes from water. MC is a thermally driven membrane baseed sepration process, in which porous hydrophobic membrane is used for sepration. MD haas the ability to use low grade and inexpensive heat sources, smaller plant footprint, and lower capital costs than conventional distillation processes.
Working Principle
In MD process, a microporous hydrophobic membrane is in contact with an aqueous heated solution on one side (feed or retentate). The hydrophobic nature of the membrane prevents a mass transfer in liquid phase and creates a vapor–liquid interface at the pore entrance. Only molecules of vapor are permitted to penetrate into pores of the microporous membrane. Vapor pressure difference across the membrane is a driving force in this process which is caused by temperature difference across the porous membrane. These molecules of the volatile compounds move across the membrane pores, and are condensed and on the opposite side (permeate or distillate) of the system.

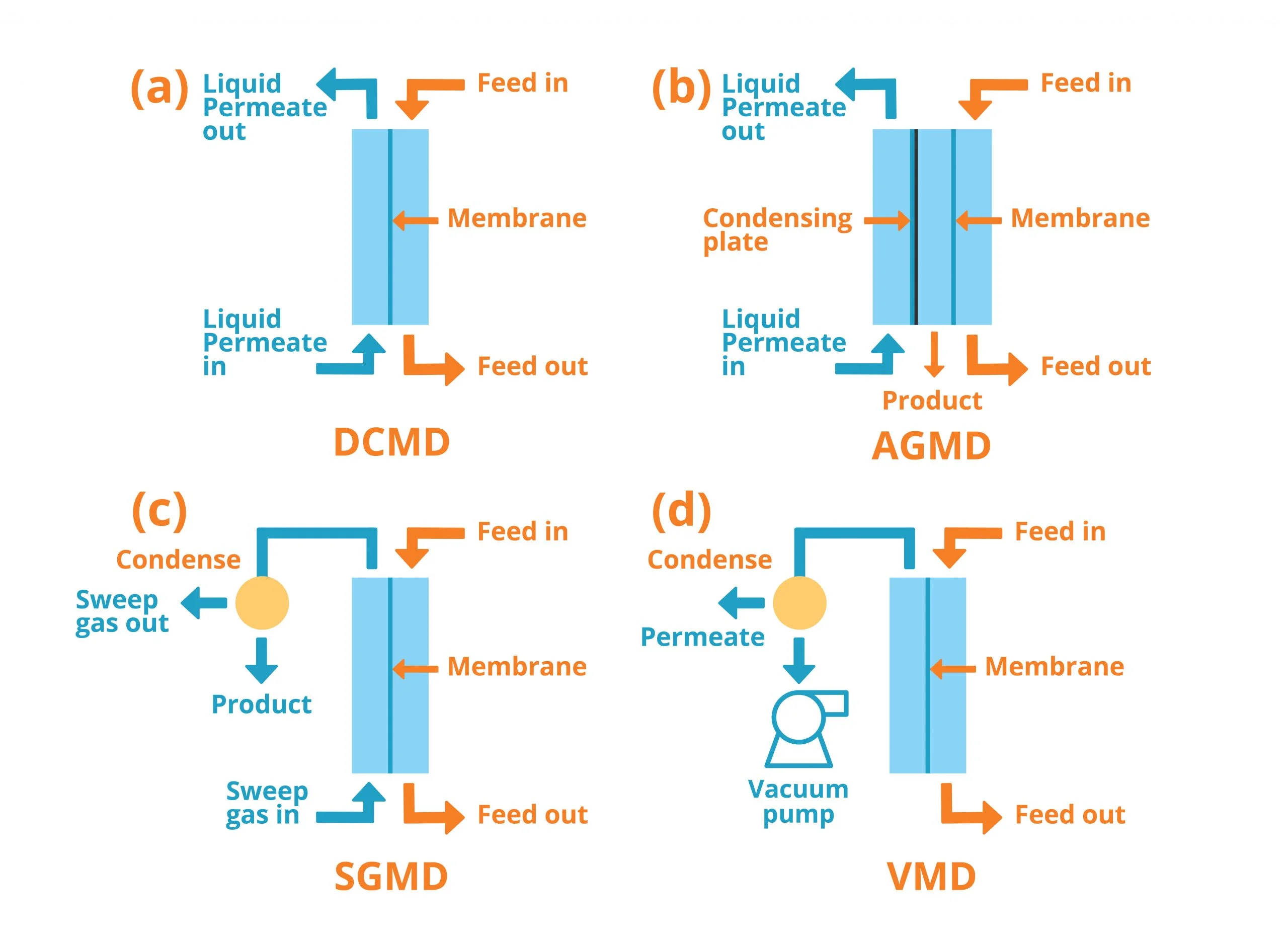
Process Setup
Among MD processes, variations exist as to the method by which the vapor is recovered once it has migrated through the membrane. MD systems can be configured in a number of ways, depending on the nature of the cold side of the membrane. In direct contact MD (DCMD) the membrane is in direct contact with the feed on one side and permeate on the other. While in air gap MD (AGMD) an air gap is interposed between the membrane and a cold condensation surface are perhaps most appropriate for desalination applications. Other configurations, such as vacuum MD (VMD) and sweeping gas MD (SGMD) methods, are typically used for stripping of volatile organics or dissolved gases.
Applications
MD can be used for the production of distilled water and for concentrating aqueous solutions. De-salting sea water and the production of clean water from brackish water are the most common MD applications because non-volatile ionic particles are almost completely retained.
MD is used for the water purification in the pharmaceutical, chemical and textile industries, for the concentration of fruit juices and milk processing, in bio-medical applications like the removal of water from blood, in the concentration of cooling liquids (glycols), non-volatile acids and oil-in-water emulsions and applications where high temperature processing causes thermal degradation of the process flow. MD can be used for the treatment of textile industry wastewater that is contaminated with dyes.


Solutions
Petro Sep has developed AQUA-SEP™ that is based on the VMD principle for separation.
Petro Sep is right for you if you are looking for:
- Turnkey solutions, from research, engineering to fabrication and operations management, utilizing various membrane-based separating technologies.
- High purity 99.5%+
- Development of custom membrane-based separation systems for a variety of applications for food, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, oil & gas, wastewater treatment industries and more.
- Conversion of seawater, river water, canal water, well-water and brackish water into drinking water.
- Our technical expertise and experience excel in solving challenging and complex separation problems.
